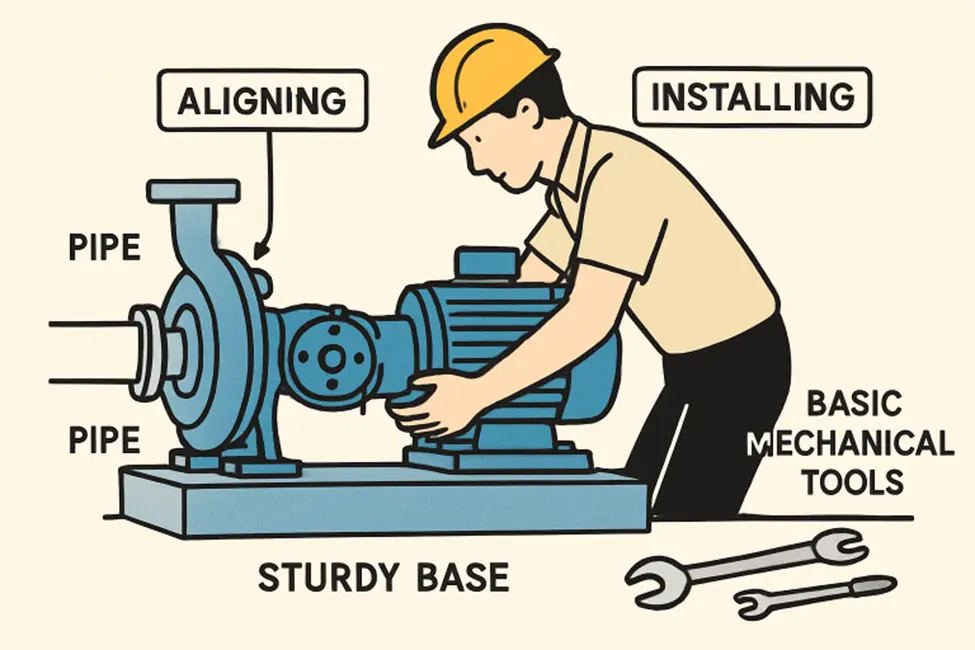
Why System Performance Depends on Accurate Pump Installation
The integrity of any fluid handling or mechanical system relies heavily on the way pumps are installed. From large municipal water plants to critical manufacturing lines, a pump’s installation determines how effectively it operates, how frequently it will require maintenance, and whether costly disruptions might occur. Precise installation underpins not just daily operations, but also a facility’s safety and overall cost management. For those looking to build more resilient pump-based systems, it’s worth pausing to learn more about the right installation processes guided by industry best practices.
Even small missteps during installation can have dramatic consequences. Poorly aligned or inadequately supported pumps are more likely to fail prematurely, increase vibration, cause noise complaints, spike energy usage, and potentially damage expensive system components. Preventing these issues at the outset leads to a longer equipment lifespan and a more predictable, manageable operating budget.
Main Steps in Professional Pump Installation
A successful pump installation follows a systematic process. It begins with a thorough site assessment to evaluate environmental and operational conditions. Next, the team prepares a stable foundation that ensures vibrations are dampened and the pump is securely held in place. Careful alignment is performed once the foundation is ready, often using precision laser tools, to guarantee the pump and motor shafts are perfectly parallel.
The final critical step involves connecting the pump to its network of pipes and electrical systems, integrating it into the facility’s overall operation. Each connection and coupling is checked for tightness and proper orientation, which helps prevent leaks and other mechanical failures. According to the U.S. Department of Energy, embarking on a pump system assessment can reveal common opportunities for energy savings and improved longevity.
Common Pitfalls and How to Avoid Them
Improper pump installation remains a leading cause of system issues, especially in complex setups. Misalignment between pump and motor, insufficient anchoring, and poorly designed intake/outlet piping can significantly reduce flow rates and increase mechanical wear.
These pitfalls can be avoided by ensuring alignment checks before and after the pump is anchored, installing vibration isolators or pads when required, and confirming piping layout adheres to recommended specifications. Hiring experienced professionals familiar with these standards is often the best defense against future breakdowns.
The Role of Calibration and Start-Up Testing
Even a flawlessly installed pump won’t deliver its intended performance without detailed calibration and commissioning. Start-up testing involves monitoring system pressure, flow rates, temperature, and vibration levels under real operating conditions. These metrics are then compared to manufacturer specifications and system design requirements to identify discrepancies.
Skipping this step can result in reduced performance, wasted energy, and hidden issues that only surface later during production or service. Integrating calibration as a formal part of installation drives up reliability and helps organizations avoid costly adjustments and disruptions down the road.
Pump Installation and Energy Efficiency
A pump installed and calibrated accurately will run closer to its peak efficiency. The Hydraulic Institute reports that optimized installations can trim energy costs by as much as 20%, a crucial factor for facilities facing high energy prices or sustainability mandates. Energy savings aren’t only about immediate cost reductions—they also minimize wear on system components and support environmental goals.
Efficient systems are less likely to overheat or require frequent adjustments. This directly benefits organizations aiming for green building certifications or striving to lower their carbon footprint.
Long-Term Benefits: Reduced Downtime and Maintenance
Properly installed pumps have fewer leaks, less vibration, and longer intervals between failures. This results in less unplanned downtime, as emergency repairs become less frequent and the system becomes easier to manage. These benefits mean better service delivery and lower long-term operating costs for industrial plants or public water utilities.
Over the years, consistent performance has reduced the total cost of ownership for pumps and auxiliary systems, helping facility managers allocate maintenance budgets more efficiently and plan for gradual upgrades rather than unexpected fixes.
Best Practices for Pump System Reliability
- Inspect all pumps and associated systems for wear, leaks, or unusual noises.
- Maintain detailed installation, calibration, and maintenance logs for each pump.
- Train operators and technicians to recognize early warning signs of pump issues.
- Use only manufacturer-recommended parts and adhere strictly to installation guidelines.
- Schedule and stick to a preventive maintenance program to catch small problems before they escalate.
Recap: Getting Pump Installation Right the First Time
Focusing on accurate pump installation brings tangible benefits: more reliable performance, reduced maintenance costs, fewer breakdowns, and sustained efficiency over the pump’s lifespan. The upfront effort of detailed planning, professional execution, and rigorous calibration pays dividends in system stability and financial savings. Whether upgrading an existing operation or launching a new project, prioritizing proper pump installation remains a cornerstone of high-performance infrastructure. Consider consulting with experienced professionals—or learning more—to ensure your next installation sets the foundation for years of dependable service.
Also Read-Balance Your Life and Your Budget: Essential Money Management Strategies